Metannogen documentation
Note: Documentation is also available from the Help-menu in the running application. An online version of the documentation can be viewed here: ManualDatasets and annotations of reactions
Datasets/annotations of reactions contain expert opinion entered by curators in form of structured information or free text. Depending on whether reactions of an existing network are annotated or whether a new network is reconstructed the term "reaction" or "dataset" is used, respectively.Annotating existing networks
In case Metannogen is used to annotate an already existing network, a dataset annotates a reaction with the same identifier. Datasets that annotate reactions of a network will be called "annotations". Conversely, datasets with IDs not matching any reaction in the network are found in the container "Datasets not annotating a reaction". Networks are displayed in the left part of the application as a browsable tree. It is shown in a tabbed pane since more than one networks may be loaded at a time. Reactions appear as child nodes of pathways. Annotations for reactions can be created with the context menu. The context menu is opened by right clicking the tree node of a reaction. Annotated reactions are indicated by a traffic light sign. Annotations are displayed and can be edited in the right part of the application window when the tree node of an annotated reaction is activated. There are text fields, toggle buttons and choice menus for the curator to enter and modify the text-fields of the annotation. Each dataset is saved as one single plain text line with tab separated text fields. Consequently, the information is stored independently of the SBML-file to be annotated. In single-user mode all dataset lines are stored in one single text file on the user's hard-disk. In multi-user mode, each dataset is stored in its own file on the server. The file name is the dataset ID.Metannogen as a primary network reconstruction tool
If Metannogen is used to reconstruct a metabolic network, the information for one reaction or a class of reactions is contained in a dataset. Usually each dataset describes one biochemical conversion in one or several subcellular compartments. Some enzymes and transport carriers are unspecific. To avoid redundancy and to reduce typing, the syntax can be used. Brace expansion provides a compact form for expressing several different but similar biochemical conversions within one single dataset. See Metannogen brace expansion for details.The resulting network consisting of metabolites and reactions can be exported as or any user defined format such as SQL and . The SBML-export allows further analysis such as or analysis in programs like Copasy. Metannogen is very flexible concerning adaptations of the output format towards special needs.
Multi-user mode
When several people work on the same project, the data can be kept on a Web-server. There are two options:- A user can register a project on the www.bioinformatics.org server in the start dialog of Metannogen. The server will return a password.
- Repository may be created on any Web server with PERL or PHP. This is explained in a tutorial.
Different identifier systems
The loaded networks might use different identifier systems for metabolites. This problem is solved by dictionaries to translate the identifiers. With the default Web-start link, the dictionary for translating Palsson-group type identifiers into Kegg is loaded. For example the dictionary contains the line "pyr C00022" telling that the metabolite identifier "pyr" corresponds to the identifier "C00022". Both denote Pyruvate. By explicitely mapping the metabolite identifiers of Palsson-group and Kegg networks, the reactions are indirectly assigned. When users choose the context menu item "Find reactions with same stoichiometry" on for example Lactate-dehydrogenase (LDH), they would find two objects: The LDH in Kegg and the LDH in the Palsson network.These dictionary files are loaded with the program option -dictionaryOfSpecies. Above mapping would be realized by the text line
pyr C00022
Resolving names of metabolites
Dictionary files can be provided with the program parameter "-names" to translate metabolite IDs into human readable names such as
...
C00022\tPyruvate
C05928\t10-Formyltetrahydrofolyl
C05931\tN-Succinyl-L-glutamate
...
In addition or alternatively, another network can be loaded.
Metannogen will also use the metabolite names in all loaded networks.
Cross-references:
Metannogen provides customizable references to various databases to allow documentation of the sources of evidence for the reaction under consideration. Some cross-references are automatically generated. Others can be entered during the network reconstruction to explain the curator's opinions. Due to its many functions regarding cross-references and browsing existing networks, it can be conveniently used just as a browser for Kegg or other networks.Graphical pathway maps:
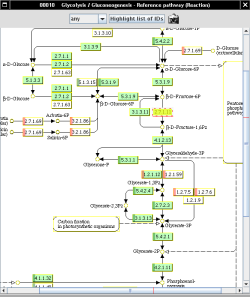
provides graphical Pathway views which are used in Metannogen to map reactions and metabolites graphically. The progress of reconstruction particular metabolic pathways can be followed since those reaction boxes in the graphical pathway maps are highlighted for which an equivalent reaction exists in the network under reconstruction. Metabolite circles for which a transport reaction is defined are also highlighted. All objects in the graphical maps have a context menu and a . They can be selected which is indicated by . In addition KEGG provides image files of single metabolites. They appear when the mouse is over a metabolite name or metabolite identifier in a text-component of the graphical user interface or when the mouse is over the metabolite circle in the graphical pathway map.Literature management:
Metannogen comes with a powerful publication management system. It is based on semi-automated association of publication full text files in PDF format with Pubmed IDs. Downloaded full text files are shared by all curators. Text expression higlighting and search includes the abstract text as well as the full text. The publication management is also available in form of a smaller program package that starts much faster then Metannogen: Webstart only publication manager.Typing aids: When writing annotation text in the multi line text field of datasets, tab-word-completion is convenient and avoids mistyping of long words. For example metabolite names are sometimes complicated. Consider a long metabolite name such as "UDP-N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanyl-D-glutamate". It is hard to type such complicated words without error. But with word expansion one does only need to type the first few letters like "UDP-N-a" and hit the tabulator key once or a few times until the desired word appears.